Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Norito; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Fujimura, Yuki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Materials, 17(3), p.547_1 - 547_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Chemistry, Physical)Natural monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite) was irradiated with 340-MeV Au ions, and the irradiation-induced nanostructures (i.e., ion tracks and nanohillocks) were observed using transmission electron microscopy. The diameter of the nanohillocks is approximately 10 nm, which is similar to the maximum molten region size calculated using the analytical thermal spike model. Ion tracks are imaged as strained regions that maintain their crystalline structure. The cross-sections of most of the ion tracks are imaged as parallelopiped or rectangular contrasts as large as 10 nm. These results strongly indicate that the molten region is recrystallized anisotropically, reflecting the lattice structure. Furthermore, low-density track cores are formed in the center of the ion tracks. The formation of low-density track cores can be attributed to the ejection of molten matter toward the surface.
Amekura, Hiroshi*; Chettah, A.*; Narumi, Kazumasa*; Chiba, Atsuya*; Hirano, Yoshimi*; Yamada, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
Injecting high-energy heavy ions in the electronic stopping regime into solids can create cylindrical damage zones called latent ion tracks. Although these tracks form in many materials, none have ever been observed in diamond, even when irradiated with high-energy GeV uranium ions. Here we report the first observation of ion track formation in diamond irradiated with 2-9 MeV C fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which
fullerene ions. Depending on the ion energy, the mean track length (diameter) changed from 17 (3.2) nm to 52 (7.1) nm. High resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (HR-STEM) indicated the amorphization in the tracks, in which  -bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
-bonding signal from graphite was detected by the electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS).
Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Idesaki, Akira*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Ikeda, Takashi*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(49), p.23628 - 23633, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Tamura, Kazuhisa
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(46), p.22733 - 22739, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)The underpotential deposition of Bi on Au(111) electrode in 1 M HClO solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO
solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi
and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi rather than the electrical double layer structure.
rather than the electrical double layer structure.
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 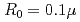 m.
m.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.928 - 931, 2023/11
J-PARC initiated the operation of the high-intensity rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H
) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H
beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H
beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H
ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Wada, Motoi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.392 - 395, 2023/11
Negative hydrogen (H ) ion sources which are used at high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC or neutral beam injection system for plasma heating in the fusion devices such as ITER produce plasmas by using RF sources driving with the frequency of 1-2 MHz. We have shown that the H
) ion sources which are used at high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC or neutral beam injection system for plasma heating in the fusion devices such as ITER produce plasmas by using RF sources driving with the frequency of 1-2 MHz. We have shown that the H beams extracted from the RF-driven H
beams extracted from the RF-driven H ion source with the frequency of several MHz have some fluctuations with the frequency of the fundamental and second harmonics. The reason is that the high plasma density is produced in the ion source with the low driving frequency. Therefore, we propose the driving RF frequency same as the RF sources with that of 324 MHz in the J-PARC linac, which is much higher than the ion plasma frequency, is used for producing the plasma to suppress the H
ion source with the frequency of several MHz have some fluctuations with the frequency of the fundamental and second harmonics. The reason is that the high plasma density is produced in the ion source with the low driving frequency. Therefore, we propose the driving RF frequency same as the RF sources with that of 324 MHz in the J-PARC linac, which is much higher than the ion plasma frequency, is used for producing the plasma to suppress the H beam fluctuations. As a first step, we performed a design of a matching circuit for the higher frequency driven H
beam fluctuations. As a first step, we performed a design of a matching circuit for the higher frequency driven H ion source. We present the background for decision of a new RF amplifier with much higher frequency and the design results.
ion source. We present the background for decision of a new RF amplifier with much higher frequency and the design results.
Hirano, Tatsumi*; Maeda, Takehiro*; Murata, Tetsuyuki*; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Matsubara, Eiichiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Takamatsu, Daiko*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(5), p.345 - 353, 2023/10
no abstracts in English
Tomita, Ryohei; Tomita, Jumpei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka
Hosha Kagaku, (48), p.1 - 15, 2023/09
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is the method to detect secondary ions produced by the sputtering of primary ions. SIMS is one of effective method to measure isotopic composition of particles containing nuclear material in environmental sample for safeguards. We are a group member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)'s network of analytical laboratories and have developed analytical techniques using SIMS and other mass spectrometers for nuclear safeguards. We will introduce the principle of SIMS and analytical techniques developed by our group to measure isotopic composition of uranium particles which having a particle diameter of micron order in environmental sample for safeguards.
 solution in the gigapascal pressure range
solution in the gigapascal pressure rangeYamaguchi, Toshio*; Fukuyama, Nami*; Yoshida, Koji*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Liquids, 3(3), p.288 - 302, 2023/09
We report the structure of an aqueous 2 mol/kg MgCl solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg
solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl
forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl
due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl
solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
Harii, Kazuya*; Umeda, Maki; Arisawa, Hiroki*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Sato, Nana; Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(7), p.073701_1 - 073701_4, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Nakagawa, Sohei; Matsuda, Makoto
JAEA-Conf 2022-002, 146 Pages, 2023/03
"The 34th Meeting for Tandem Accelerators and their Associated Technologies" was held on July 21-22, 2022 organized by Nuclear Science Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This meeting was held only on-line for preventing the spread of COVID-19 infection. The purpose of this meeting is contribution of development for related technology and of management of facilities through exchange of information among the researchers and engineers using and operating electrostatics accelerator facilities like tandem accelerators. There were 25 presentations which contains current status report of facility, technical development of accelerator, research of application. The total number of participants was a hundred, from 26 universities, research organizations and industries. This meeting consisted of only oral session, a poster session was not carried out because of on-line meeting. This proceeding compiles the contents of report papers in the meeting.
Sato, Tetsuya; Nagame, Yuichiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 78(2), p.64 - 72, 2023/02
The study of the chemistry of superheavy elements, which are located in the heavy extremes of the periodic table, has made considerable progress over the past 20 years, and new approaches based on various ideas have recently been developed. Research groups in Japan have also made significant contributions to the development of research on superheavy elements. Recently, notable results have been reported for the transactinide elements rutherfordium (element 104), dubnium (element 105), and seaborgium (element 106), and the heavy actinides with atomic numbers exceeding 100. The review will focus on the recent main results of these elements. This review outlines the main recent results and touches on future prospects.
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.675 - 679, 2023/01
In J-PARC, we have been conducting the test of a J-PARC-made internal antenna in order to establish the production method and understand the beam characteristics of the antenna. At this time, we investigated the outgas characteristics during the production of a high-density plasma by using the J-PARC-made antenna. It is confirmed that no remarkable impurities are emitted from the antenna by a residual gas analysis using a quadrupole mass analyzer installed downstream the ion source and a spectroscopic analysis of the plasma in the ion source. It is found that the emittances of the H beam extracted from the J-PARC radio-frequency H
beam extracted from the J-PARC radio-frequency H ion source by using the antenna was similar as those in case by using SNS antenna.
ion source by using the antenna was similar as those in case by using SNS antenna.
Shibata, Takanori*; Ishida, Masaki*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.863 - 867, 2023/01
Continuous operation duration of the J-PARC Radio Frequency (RF) ion source has been extended step by step these years for the goal to supply stable beam during the entire period of J-PARC user operation (around 7 months) each year. A 3651 hours (5 months) continuous ion source operation has been achieved from Nov. 2020 to Apr. 2021. As the lifetime of the ion source is mainly limited by failure on the RF antenna coil, detailed evaluation of the antenna surface condition is required to ensure the feasibility of the further extension of the operation time. In the present study, dimension measurements and SEM/EDS analyses were applied to understand the surface discoloration of the RF antenna. The discoloration after the long-term continuous operation is due to deposition of injected cesium (for H surface production process) and of stainless used steel (Fe, Cr, Ni) from the ion source components sputtered by plasma. The results show that the enamel coating of the RF antenna has not worn out in the long-term continuous operation for several months and, hence, extension of the ion source continuous operation duration can be extended.
surface production process) and of stainless used steel (Fe, Cr, Ni) from the ion source components sputtered by plasma. The results show that the enamel coating of the RF antenna has not worn out in the long-term continuous operation for several months and, hence, extension of the ion source continuous operation duration can be extended.
Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Matsuda, Makoto; Nakamura, Masahiko; Ishizaki, Nobuhiro; Kutsukake, Kenichi; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Asozu, Takuhiro; Matsui, Yutaka; Nakagawa, Sohei; Abe, Shinichi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1109 - 1113, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Nii, Keisuke*; Ida, Yoshiaki*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamaguchi, Takanori*; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Harada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.601 - 604, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Jinno, Satoshi; Fujita, Natsuko; Tanuma, Hajime*
Dai-23-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.89 - 92, 2022/12
The measurement of chlorine-36 ( Cl) in AMS, which is important for the dating of saline groundwater, is more difficult than other nuclides due to the isobaric interference by sulfur-36 (
Cl) in AMS, which is important for the dating of saline groundwater, is more difficult than other nuclides due to the isobaric interference by sulfur-36 ( S). In general, acceleration voltages of 6 MV or higher are required to separate
S). In general, acceleration voltages of 6 MV or higher are required to separate  Cl and
Cl and  S. Therefore, this study aims to develop an ion funnel reaction cell and incorporate it into the low energy side of JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV to selectively suppress
S. Therefore, this study aims to develop an ion funnel reaction cell and incorporate it into the low energy side of JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV to selectively suppress  S.
S.
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(2), p.63 - 81, 2022/12
The understanding of the swelling phenomenon of montmorillonite is essential to predict the physical and chemical behavior of clay-based barriers in radioactive waste disposal systems. This study investigated the key factors controlling crystalline swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. On the basis of the comparisons between MD simulated and experimental results, the water content in the interlayer in five homoionic (Na , K
, K , Cs
, Cs , Ca
, Ca and Sr
and Sr ) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
) montmorillonite was strongly correlated to the hydration number and the preference of an outer- or inner-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The detailed analysis for these results offer insights that the hydration number is controlled by the hydration free energy, the volume and the distribution of each interlayer counter-ion. The systematic MD simulations with virtually variable parameters clarified that the hydration free energy and the charge of interlayer counter- ions compete as influencing factors, and the control the formation rate of an outer-sphere complex of each counter-ion. The empirical relationships between these key factors will allow essential insights into predicting the swelling behavior of montmorillonite with different interlayer counter-ions.
Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Yoshida, Koji*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 365, p.120181_1 - 120181_10, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.81(Chemistry, Physical)Neutron scattering measurements were performed on an aqueous 3 mol/kg NaCl solution in D O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.
O at temperature and pressure conditions of 0.1 MPa/298K, 1 GPa/298K, 1 GPa/523K, and 4 GPa/523K. The empirical potential structure refinement method was applied to the obtained data to extract the pair correlation function, coordination number distribution, angular distribution (orientation correlation), and spatial density function (3-D structure). From those results, pressure and temperature dependence of solvation and association of ions and solvent-water structure were discussed.